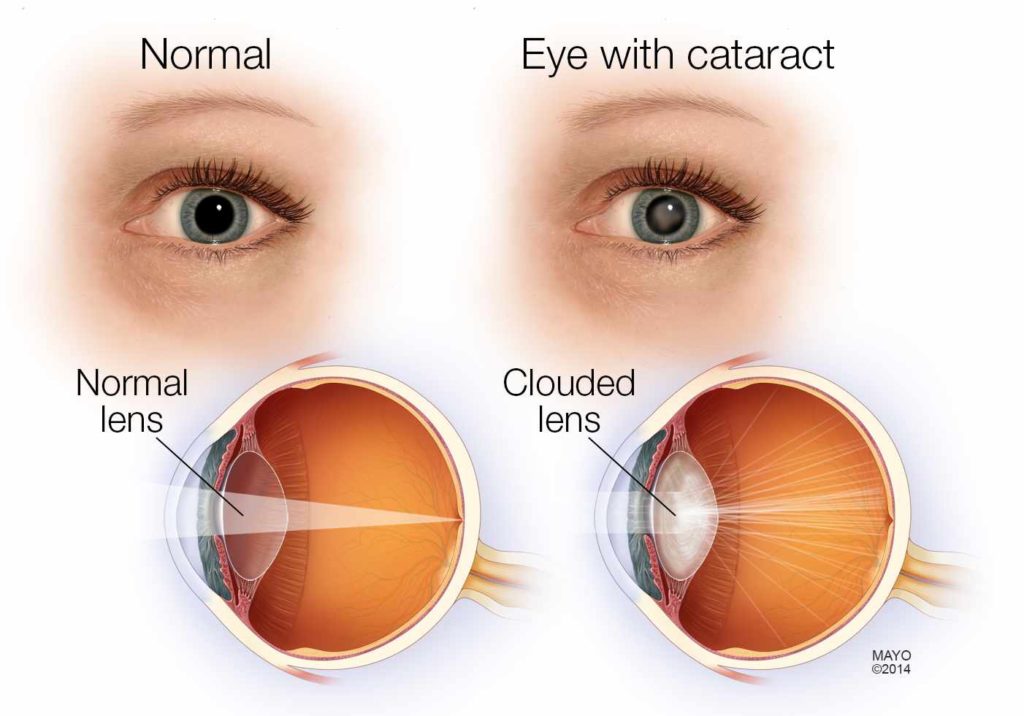
A cataract is a clouding of the lens in the eye which leads to a decrease in vision.
The annual incidence of cataract blindness is about 3.8 million in India. According to WHO/NPCB ( National Programme for Control of Blindness ); there are about 22 million blind eyes ( 12 million blind people ) in India, out of which 80.1% are blind due to cataract.
Cataract develops slowly and without any pain so a person can be unaware of its development till vision and lifestyle get affected. Symptoms may include decrease in contrast sensitivity ( faded colors ), blurry vision, diplopia ( double vision ), halos around light, trouble with bright lights, and trouble seeing at night. This may result in trouble driving, reading, or recognizing faces. Poor vision caused by cataracts may also result in an increased risk of falling and depression.
Cataracts are most commonly due to aging but may also occur due to trauma or radiation exposure, be present from birth, or occur following eye surgery for other problems. Risk factors include diabetes, smoking tobacco, prolonged exposure to sunlight, and alcohol. The underlying mechanism involves accumulation of clumps of protein or yellow-brown pigment ( urochrome ) or hydration of the lens fibres that reduces transmission of light to the retina at the back of the eye.
Diagnosis is by an eye examination.
Cataract Surgery:
Prevention
There are no scientifically proven means of preventing cataracts, however, wearing sunglasses that block ultraviolet light may slow their development. Although antioxidants (such as vitamins A, C, and E) andnutrients lutein and zeaxanthin has been thought to protect against the risk of cataracts, clinical trials have shown no benefit from supplements.
Treatment
Surgical
The need and timing of surgery depends on a person’s visual needs and other risk factors. Cataract removal can be performed at any stage and no longer requires ripening of the lens. Surgery is usually ‘outpatient’ and usually performed using local anesthesia.
Phacoemulsification is a verycommonly done cataract surgery in the world. This procedure uses ultrasonic energy to emulsify the cataractous lens into smaller pieces within its natural bag followed by a foldable intraocular lens ( monofocal/multifocal )implantation in its place through an incision as small as 2.8mm.
Extracapsular cataract extraction (ECCE) consists of removing the lens manually, through a 10- to 12-mm incision which is closed with sutures at the end of surgery. ECCE is less frequently performed than phacoemulsification, but can be useful when dealing with very hard cataracts or other situations where emulsification is problematic.
Manual small incision cataract surgery (MSICS), in which the lens is removed through a self-sealing scleral tunnel wound in the sclera which, ideally, is watertight and does not require suturing.
Intracapsular cataract extraction (ICCE) is rarely performed, in which the lens and surrounding capsule are removed in one piece through a large incision while pressure is applied to the vitreous membrane. The surgery has a high rate of complications.
Postoperative care
The postoperative recovery period is usually short. The patient is usually ambulatory on the day of surgery, but is advised to move cautiously and avoid straining or heavy lifting for about a month.
Complications
Serious complications of cataract surgery include retinal detachment and endophthalmitis. In both cases, patients notice a sudden decrease in vision, pain, unilateral visual field defects, flashes of light, or floating spots.
Less serious complications include corneal edema and cystoid macular edema and normally improve with time and with application of anti-inflammatory drops.
Posterior capsular opacification, also known as after-cataract, is a condition in which months or years after successful cataract surgery, vision deteriorates or problems with glare and light scattering recur, usually due to thickening of the back of the posterior capsule surrounding the implanted lens. Management involves cutting a small, circular area in the posterior capsule with targeted beams of energy from a laser, called Nd:YAG laser capsulotomy.
